What Are These Forms?
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
As a tax preparer, it is important to familiarize yourself with common tax forms in order to accurately and efficiently prepare tax returns for your clients. While there are many forms that you can encounter, we have listed the most common forms.
W-2: Wage and Tax Statement
The IRS requires the employer to report employee wage and salary information on Form W-2. The employer must give a W-2 form to a client every January 31st.
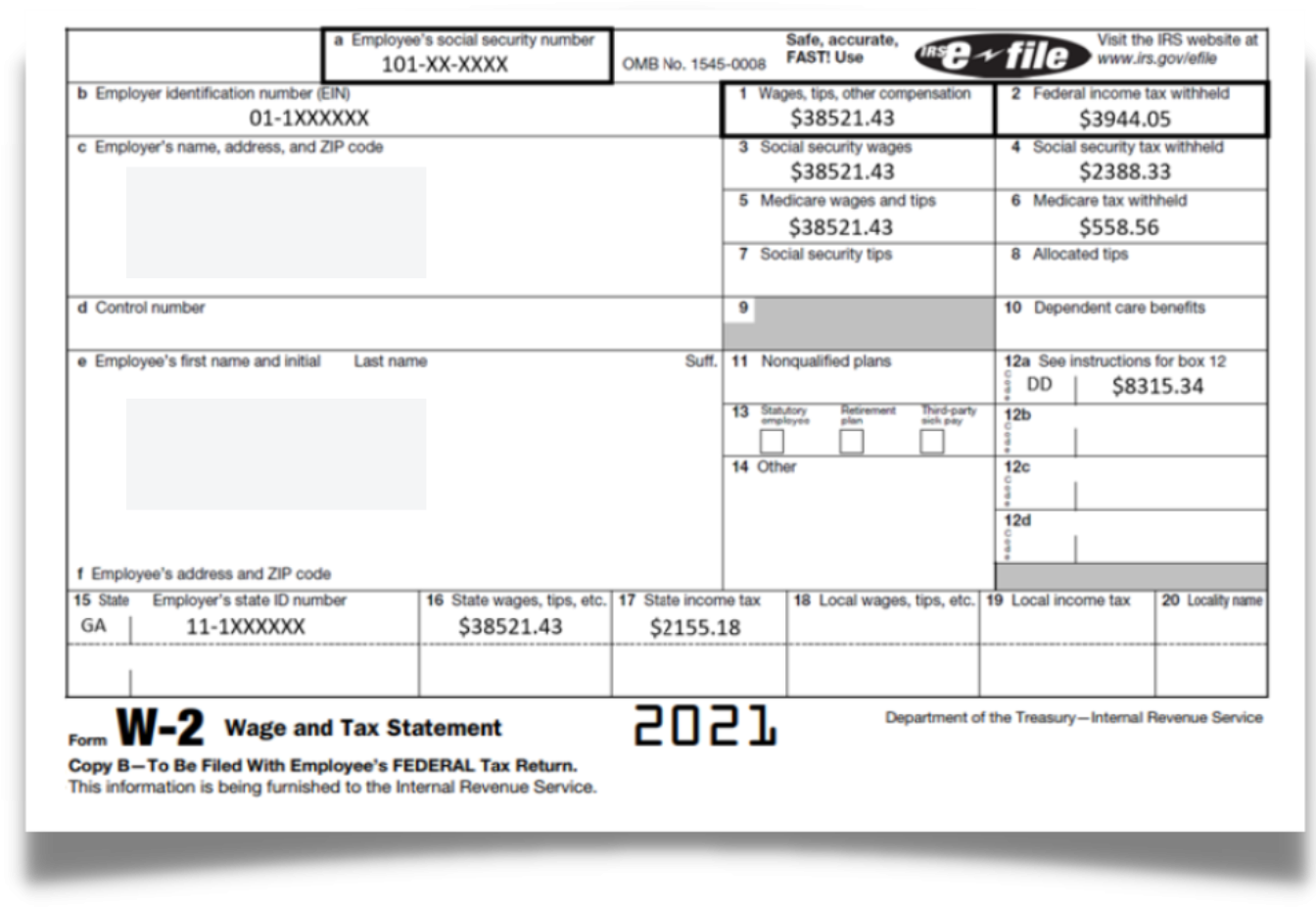
- This form shows the income.
- This form shows Federal Tax Withheld.
- This form indicates your state tax return information.
Form 1098-T: Education Form
Tuition-paying students at eligible colleges or other post-secondary institutions should receive a copy of Form 1098-T from their school each year. Eligible institutions include most colleges, universities, and vocational schools. By reporting tuition, you can get two credits on your return; the American Opportunity Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit. These can boost your return and can lower tax liability.
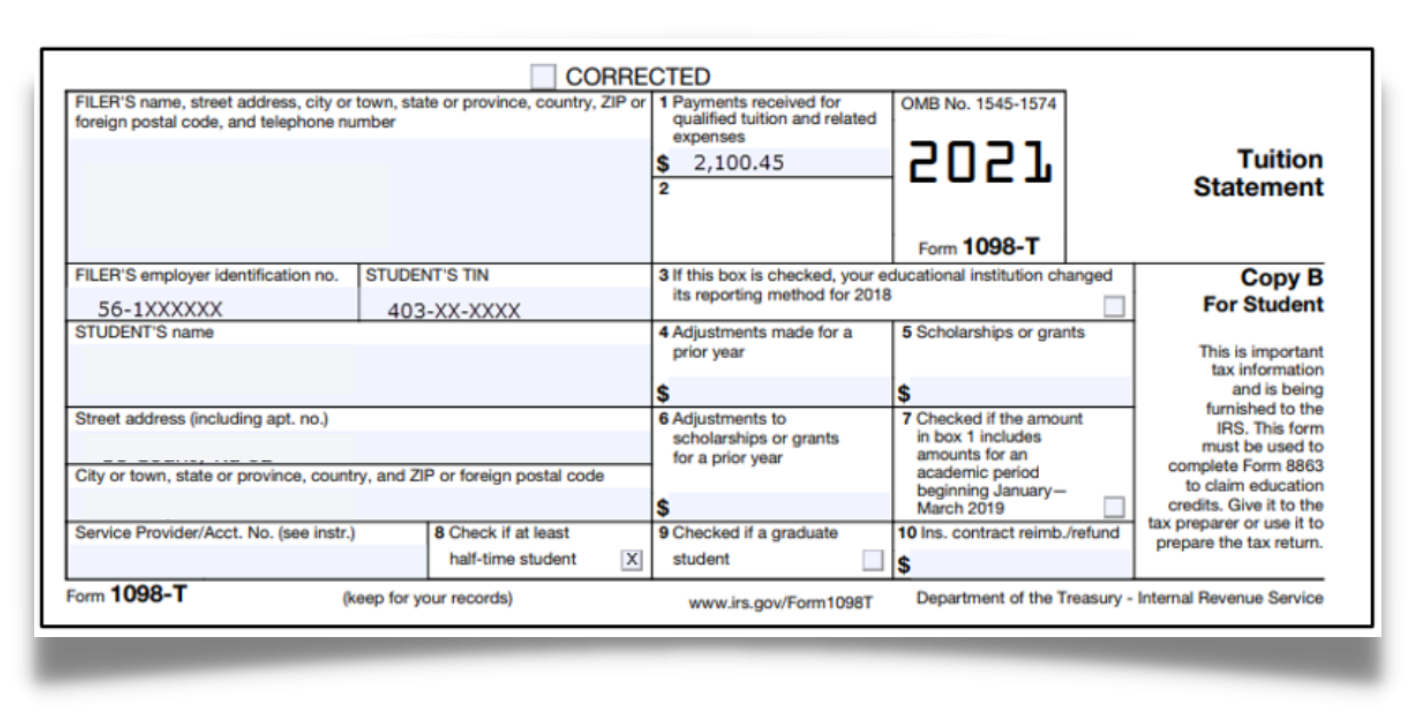
- Use this form to report tuition.
- Use this form to report scholarships.
Form 1099-MISC (Contractor or Freelance) and Form 1099-NEC (Non-Employment Compensation)
If the taxpayer is involved in a trade or business and receives payments from other people or entities, these transactions will be reported to them and the IRS. Before the tax year 2020, these payments usually appeared on Form 1099-MISC. Now, businesses must separately declare nonemployee compensation on Form 1099-NEC. Any employee payments, including income, retirement contributions, insurance payments, expense reimbursements, and travel expenses, typically go on Form W-2. Other than the change for nonemployee compensation, Form 1099-MISC remains mostly the same for payment reporting.
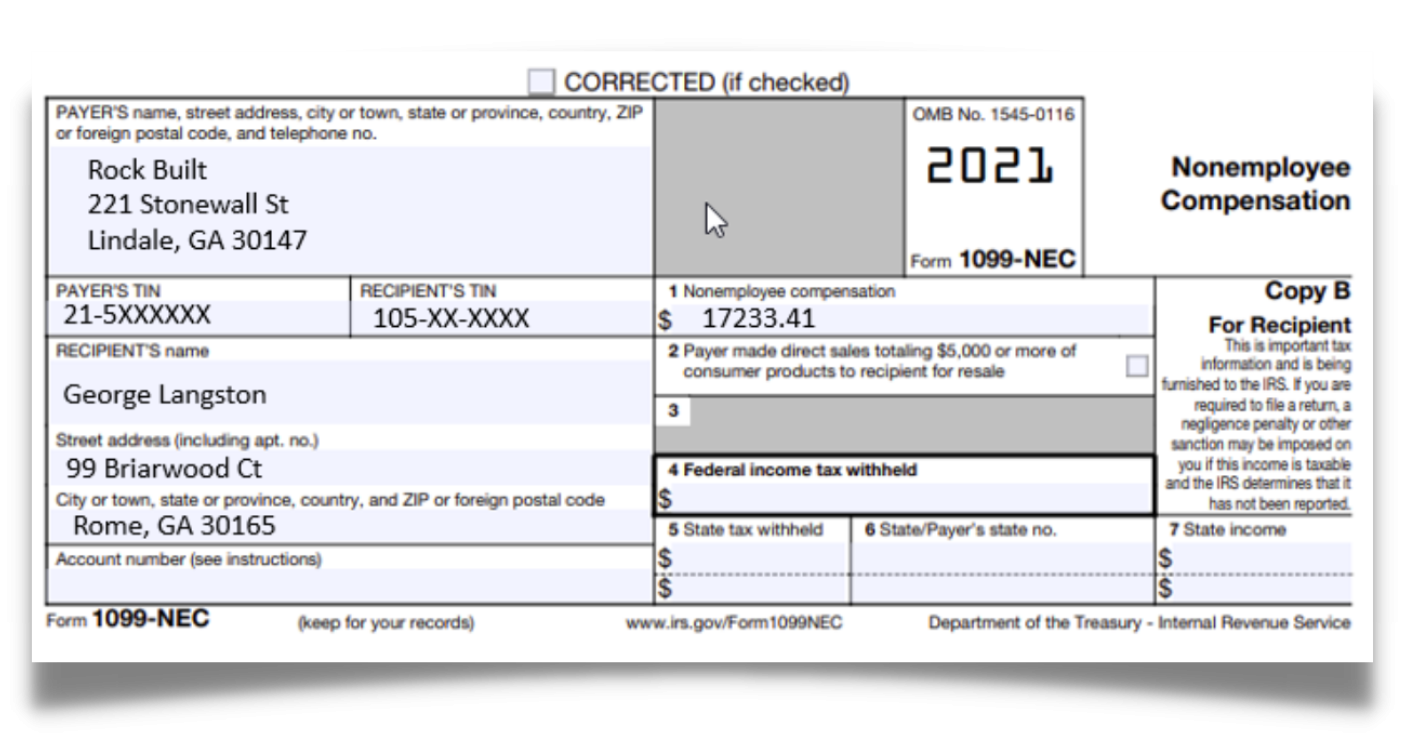
- Use this form for contracts.
- Use this form for freelance.
- Use this form for work outside of your employer.
Form 1095-A: Health Insurance in the Marketplace
If the taxpayer bought health insurance through the marketplace, they should receive a Form 1095-A, also called the "Health Insurance Marketplace Statement." The form provides information about the insurance policy, your premiums, any advance payment of premium tax credit, and the people in the household covered by the policy.
You must complete this form because you will get a refund 100% most of the time.

- Use this form for the Health Insurance that you buy for yourself from the marketplace.
Form 1098-E: Student Loans
This form is sent out by loan "services, " which collect loan payments. Loan services must send a 1098-E to anyone who pays at least $600 in student loan interest.
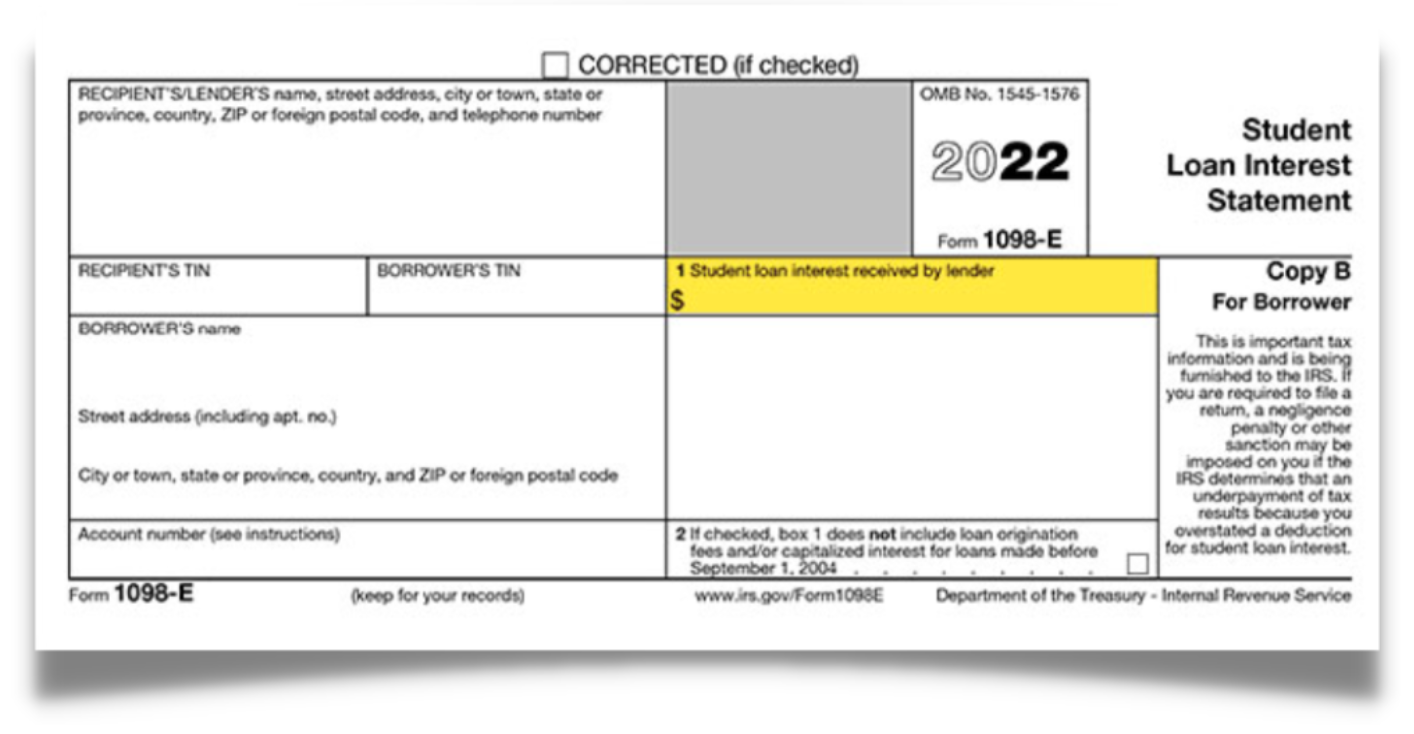
- Use this to report Student Loan Interest.
- You get the money back on the interest you pay on your student loans. So if you spend $2000 and the interest is $300, you'll get that $300 back.
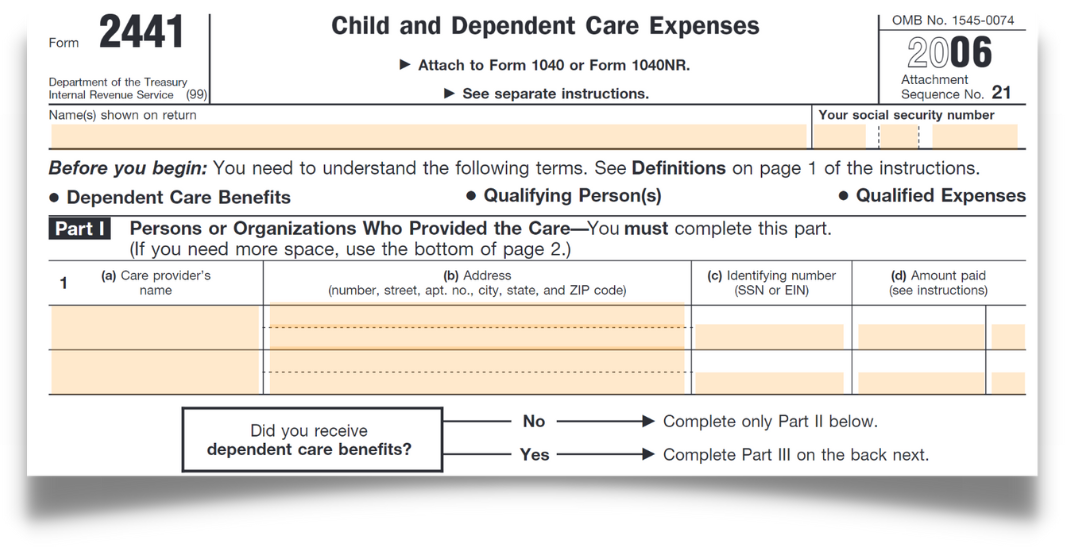
Child and Dependent Care Credit form:
The Child and Dependent Care Credit Form (Form 2441) is a tax form used to claim the Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit. This credit is available to taxpayers who pay for the care of a qualifying child or other dependent in order to work or look for work.
The form is used to calculate the credit, which is based on the amount of expenses paid for the care of a qualifying individual, and the taxpayer's income. The credit is worth up to 35% of the qualifying expenses, but the percentage varies depending on the taxpayer's income.
To claim the credit, taxpayers must provide the following information on Form 2441:
- The name, address, and taxpayer identification number (SNN or EIN) of the care provider.
- The name and relationship of the qualifying individual(s) for whom care was provided.
- The amount of expenses paid for the care of each qualifying individual.
- The number of days of care provided during the tax year.
The form should be included with the taxpayer's tax return and must be accompanied by proof of the expenses, such as receipts or cancelled checks.
It's important to note that the credit is non-refundable, which means that it can only be used to offset the taxpayer's tax liability, not to generate a refund. Also, it's recommended to consult a tax professional or the IRS website to see if the taxpayer is eligible for this credit and what are the rules and regulations that apply.
Form 1099-B: Interest
Form 1099-B is a tax form used to report information about the sale or exchange of certain securities and other financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, options, and mutual funds. This form is used to report the proceeds from the sale of these assets to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the taxpayer.
The form is used to report transactions that occurred during the tax year, and it should be sent to the taxpayer by the financial institution or broker that executed the transaction by January 31st of the following year. The taxpayer will then use the information on the form to report the transaction on their tax return.
Form 1099-B includes information such as the date of the transaction, the description and number of shares sold, the sale price, and any adjustments or costs associated with the sale. It also includes information about any wash sales, which occur when a security is sold at a loss and then repurchased within 30 days.
Form 1099-B includes information such as the date of the transaction, the description and number of shares sold, the sale price, and any adjustments or costs associated with the sale. It also includes information about any wash sales, which occur when a security is sold at a loss and then repurchased within 30 days.
The form will also indicate if the cost basis of the security is reported to the IRS, which is required for securities acquired on or after January 1, 2011, and certain securities acquired before January 1, 2011. The cost basis is the original value of an asset, used to determine the capital gain or loss when the asset is sold.
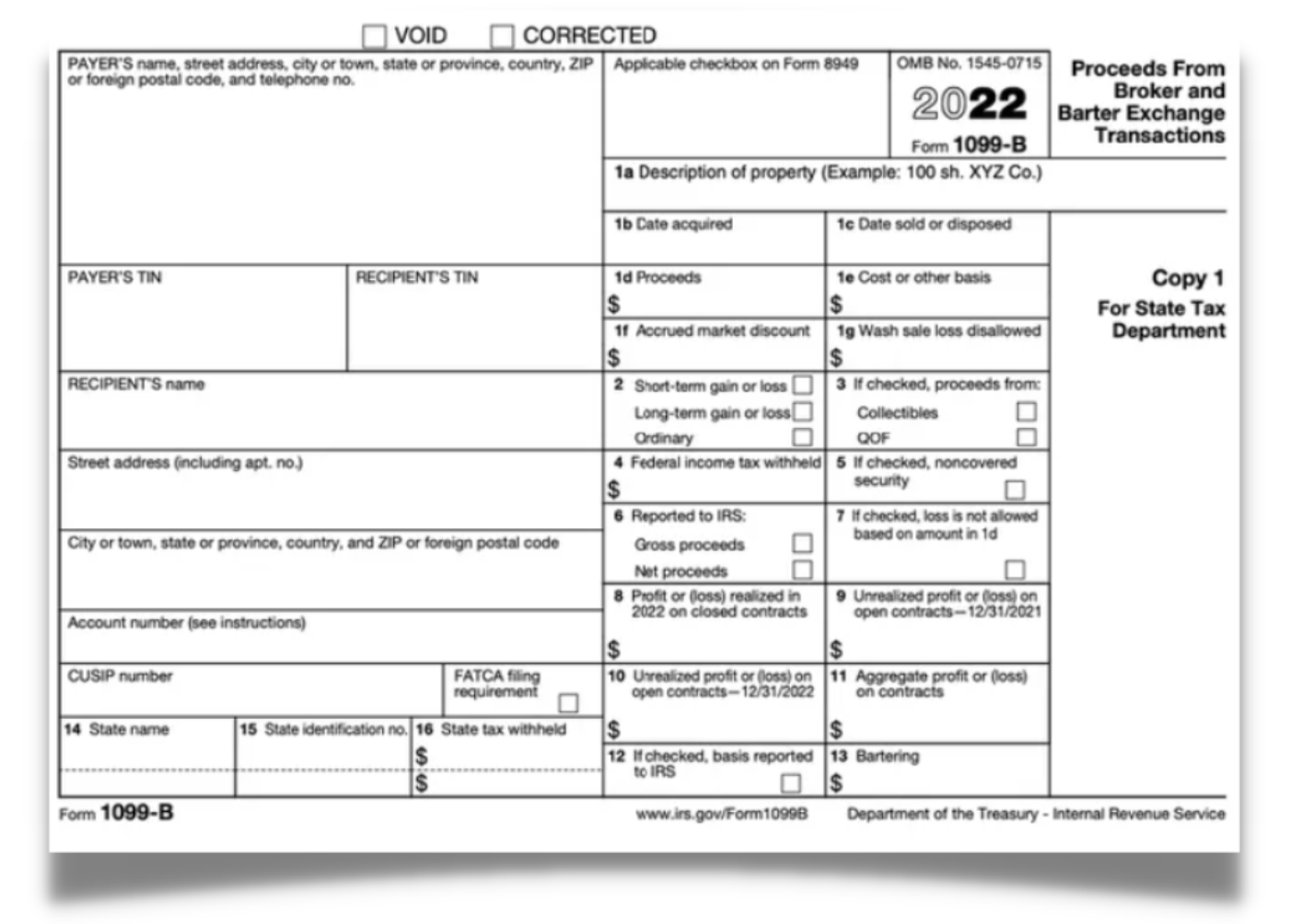
- Use to report dividends
- Use to report interest
- Use to report stocks
- Long-Term Capital Gains/Etc
Form 1099-G: Unemployment
Federal, state, and local governments may issue taxpayers Form 1099-G for certain government payments. While there are a handful of purposes for this form, it's most commonly used for two payments types:
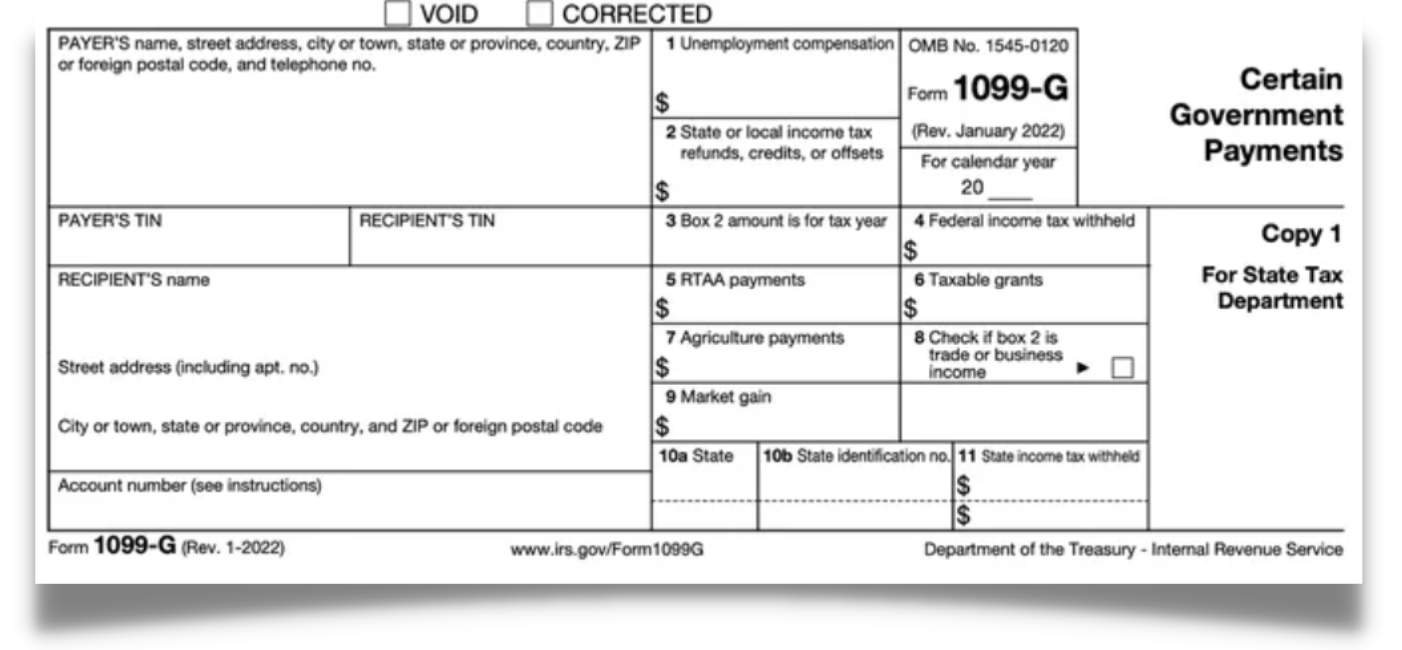
- Use for unemployment
- State and Local Government Payments
Who we are
We are committed to building people and creating world class entrepreneurs, communities and technology to make the world more efficient.
Featured links
-
Graduation
-
Courses
-
About us
-
FAQs
Get in touch
-
Your email
-
Your phone number
Connect with us
-
Facebook
-
Twitter
-
Youtube
-
Instagram
-
Linkedin
Copyright © 2024
